For information on why an SSL Certificate is required for SSL Inspection, see SSL Inspection.
In order to deploy certificates with this method, you, your school's network, and your devices will need to meet the following prerequisites:
- Your devices must be running Windows 7, Windows 8, or Windows 10
- Your network must have an Active Directory Domain
- You must have access to an Administrator account that can edit Group Policy objects.
If you are unsure about any of the above prerequisites, contact your Third Party ICT provider, who should be able to set up certificate deployment for you.
Deployment with the method outlined in this article will store the certificate into the 'Local Machine Store' of the computers affected by the group policy. This means the certificate will be available to all users who log on to that computer.
| Store Location | Use Case |
|---|
| Local Machine Store | Where the device will be used by multiple users |
| Current User Store | Where the device will be used by only one staff member/student, or where only one user may have consented to having their secure traffic inspected. |
Configuring Deployment of an SSL Certificate (as a Trusted Root Certification Authority)
1. Download the certificate file from the N4L SSL Inspection Certificate page.
2. On your Domain Controller or Technician PC, open Active Directory Group Policy Management.
The icon looks like this:

Figure 1: Group Policy Management icon
3. The Group Policy Management window appears.
Select the Organizational Unit (or OU) that contains the computers you wish to deploy the certificate to.
In this example, we will use the Win 7 > Computers OU.
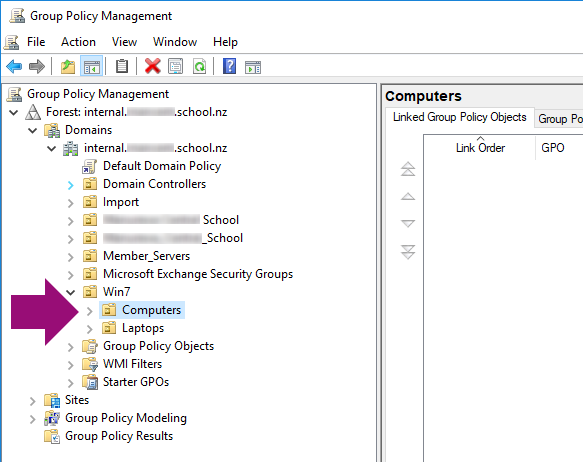
Figure 2: The Group Policy Management Window, with Computers OU highlighted
4. Right Click on the OU, and then click Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here...
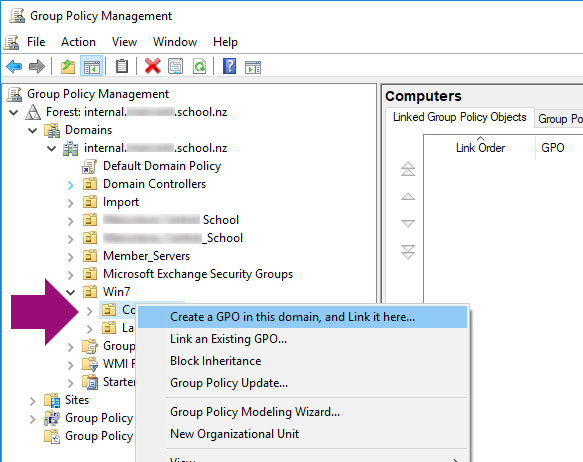
Figure 3: Creating a new GPO
5. You will be asked to name the new Group Policy Object (GPO). Enter a descriptive name, and click OK.
Here we have chosen the name 'SWI Certificate Deployment'.
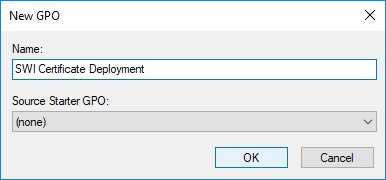
Figure 4: Naming the new GPO
6. The new GPO will appear in the Right Pane.
Right Click on the new GPO and select Edit.
Figure 5: Right Click the GPO to Edit
7. The Group Policy Management Editor window will open.
Navigate to the following location in the Left Pane:
Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Public Key Policies >Trusted Root Certification Authorities
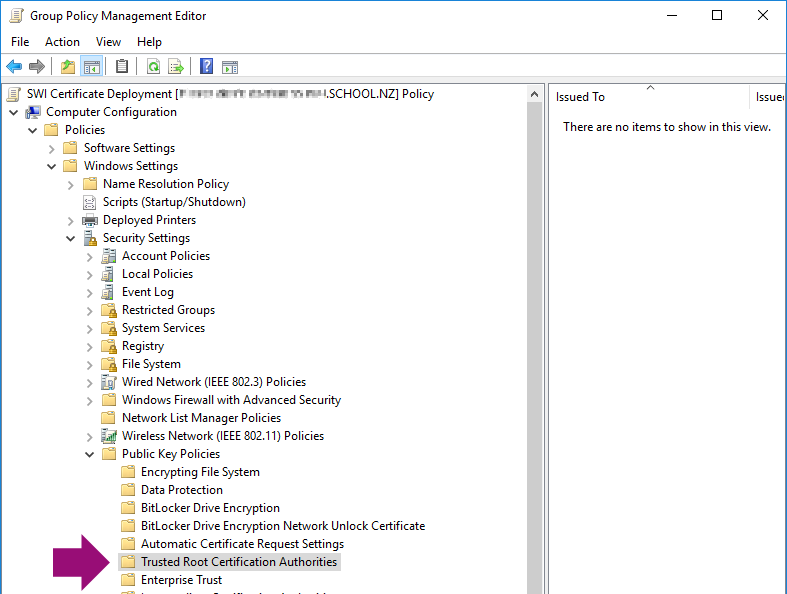
Figure 6: The GPOE Window with the location highlighted
8. Right Click on the Trusted Root Certification Authorities folder and click Import.
Figure 7: Right Click > Import
9. The Certificate Import Wizard will be shown. On the first page, Local Machine is selected for you. Click Next.
Figure 8: The Welcome page
10. On the File to Import page, click Browse and choose the certificate you downloaded in Step 1. Click Next.
Figure 9: The File to Import page
11. On the Certificate Store page, the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store should be selected. Click Next.
Figure 10: The Certificate Store page
12. The Completing the Certificate Import Wizard page is shown. Confirm that the certificate file name is correct, and then click Finish.
Figure 11: The process is complete
13. If the certificate was valid, a success message is shown. If you receive an error, the certificate file may have become corrupted - try downloading it again.
Figure 12: A successful import
Please note:
These steps and screenshots were performed on a server running Windows Server 2016.
If your server is not using Windows Server 2016 then the steps may vary, depending on the specific operating system your server is running (i.e. an earlier version of Windows Server; Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2003).
When To Perform These Steps
Installing an SSL certificate is usually required after configuring SSL Filtering for the first time, or when the certificate has expired or been re-issued.
The certificate will be deployed to any computers under the effect of the policy configured in this guide. You may need to link this policy to multiple OUs in order to deploy to all of your computers (depending on the structure of your domain).



